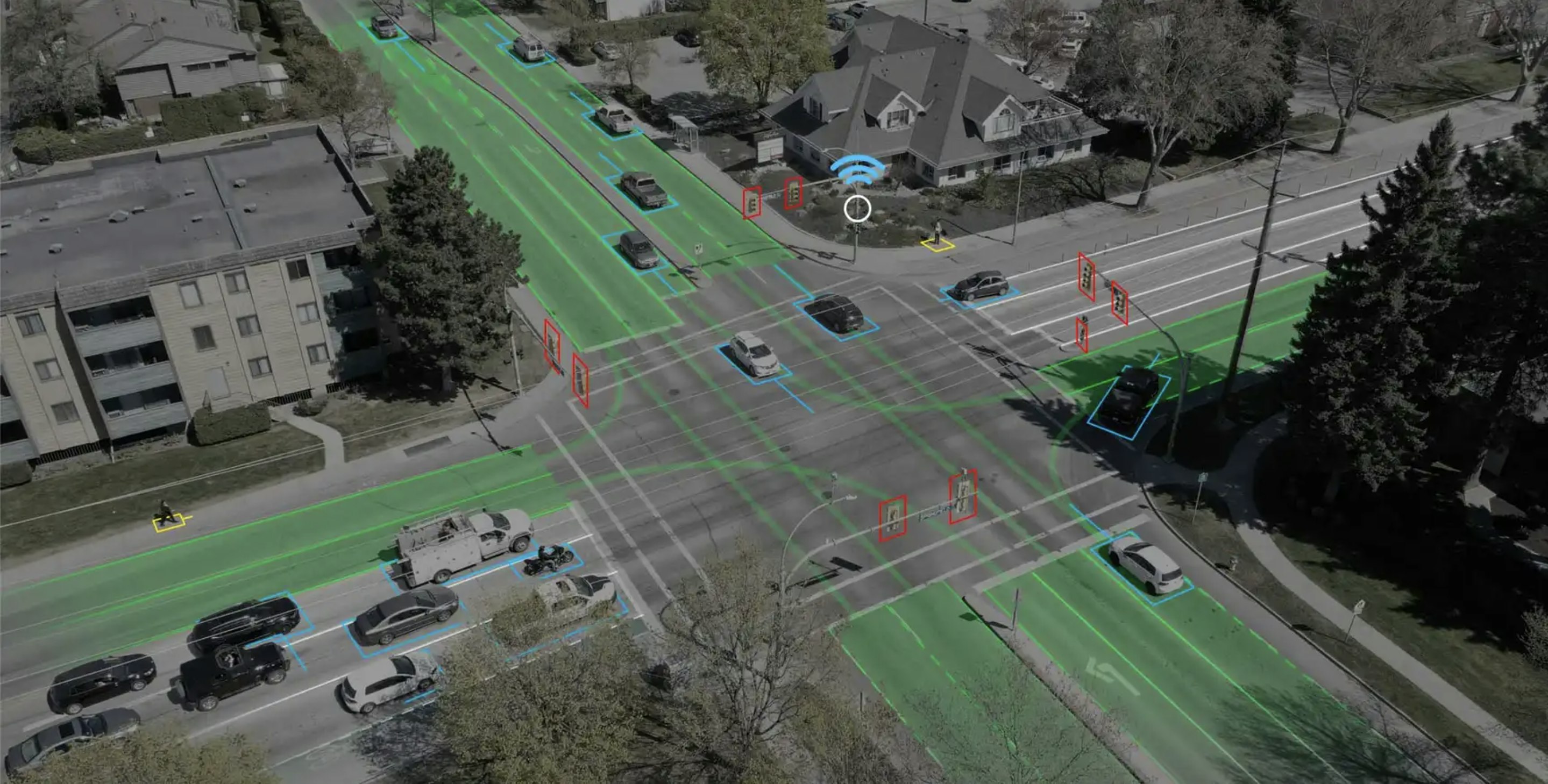
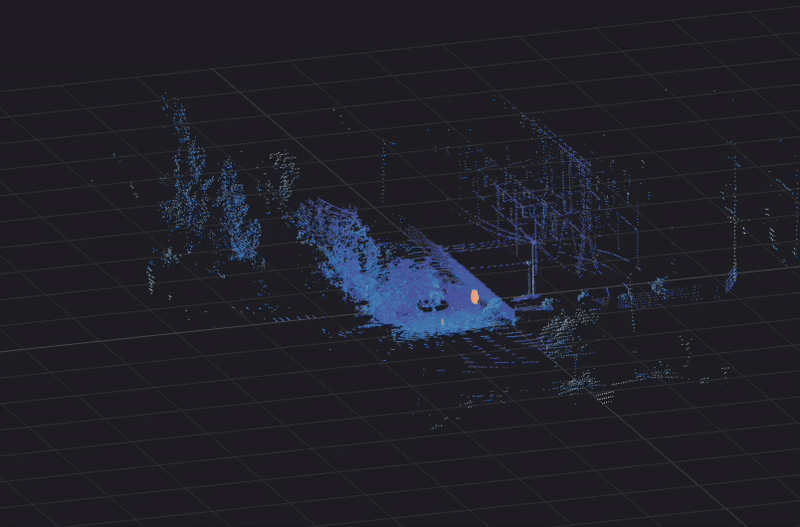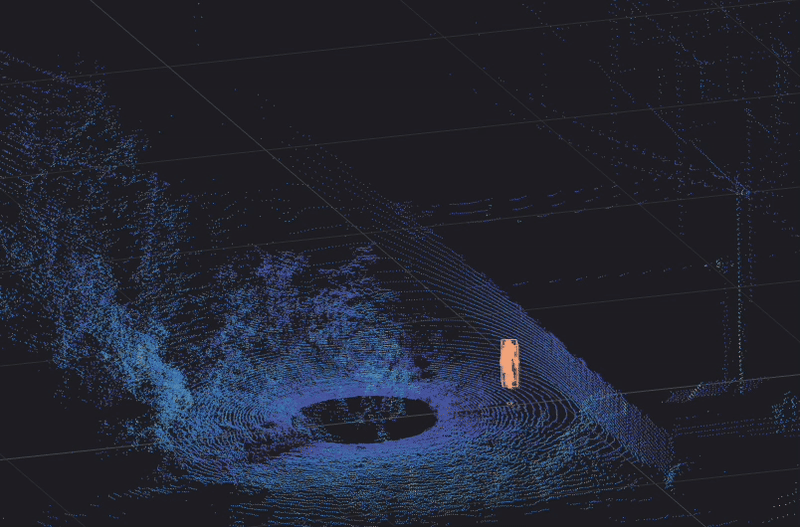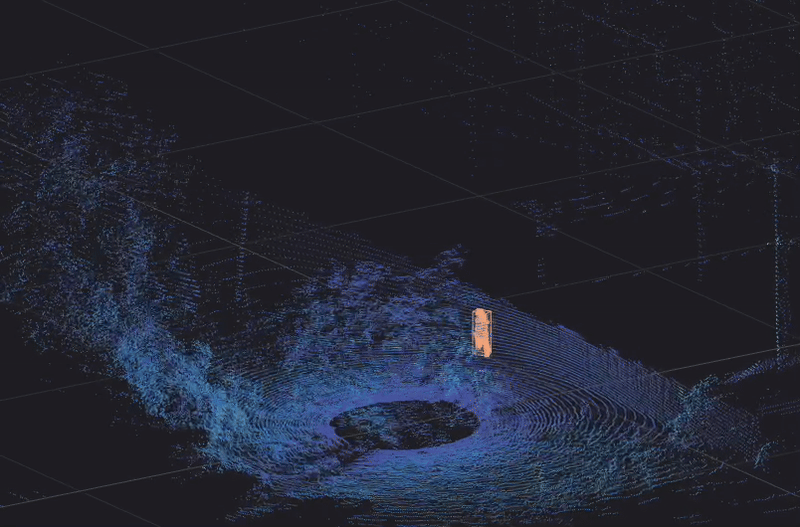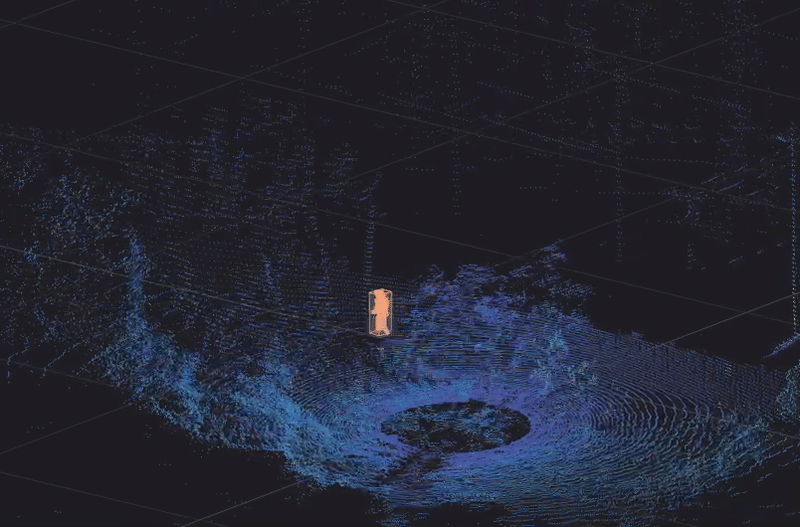
Traffic camera basics
When traffic cameras were first introduced, traffic planners and city engineers were able to get valuable information about the presence of road users at intersections and their behaviors. Traffic cameras are now used in a variety of ways, including intersection surveillance, recording red light and stop sign infractions and the monitoring of vehicles for excessive speed.
While they have been effective in significantly reducing the number of serious and fatal car crashes, they have several disadvantages and have been surrounded by controversy. Some of the drawbacks include:
- Inability to record effectively during adverse weather conditions, at night or in poor lighting
- Subject to citizens’ complaints regarding privacy violation
- Can be expensive to install and maintain
As research shows that most traffic accidents occur at night and during poor weather, new solutions to address these shortcomings are being sought out. Lidar is a technology that fills the gap by offering reliable and anonymous traffic data in any lighting or weather conditions.
When to use traffic cameras
Traffic cameras are an excellent option for incident detection and are suitable for cities in climates where adverse weather conditions are not very common. However, since cameras are not reliable in poor light or weather, they cannot provide 24/7 coverage and do not perform well in adverse weather, making them less effective for traffic management.
How does BlueCity stack up to cameras?
BlueCity, which combines 3D lidar sensors with AI software, is an ideal, cost-effective solution for transport planners, operations and road safety departments, and city engineers who need multimodal traffic data collection in all weather and lighting conditions.
BlueCity is an excellent choice in areas where substantial controversy exists regarding the collection of private citizen data. Lidar sensors capture data anonymously, effectively eliminating privacy concerns around collecting and storing data.
What’s more, BlueCity’s artificial intelligence capabilities power advanced safety analytics and offer better visualization of the data captured.
Traffic camera FAQ
Q: Can traffic cameras help with operations?
A: No. Since traffic cameras can’t supply reliable data at night or during adverse weather, they are not as useful for operations.
Q: Is privacy protected with traffic cameras?
A: No. Since cameras record everything, from vehicles, to license plates and faces, many citizens groups object to private data being captured and stored by government agencies. There is concern that more surveillance by video can lead to more opportunities for privacy abuse.
Q: Can traffic cameras tell which intersections are dangerous?
A: Yes and no. Video cameras are often used to capture incidents such as accidents on the road, so yes, they can tell you which intersections are dangerous but only after the fact. Another drawback is that cameras are not reliable at night or in poor weather, which is when most accidents occur. Once enough accidents have occurred at a particular intersection, it can be labeled as dangerous and video can be examined to see what caused the accidents. BlueCity goes a step further by providing safety analytics that can offer information such as speeding, wrong turns, near misses and more before accidents and fatalities occur, providing a proactive approach to traffic management and safety.
Traffic camera summary
Pros: Traffic cameras can provide valuable information at intersections and are used effectively for intersection surveillance, recording infractions and monitoring for speed. Their use has been effective in significantly reducing the number of serious and fatal car crashes over the years.
Cons: Cameras can be an expensive choice for installation and maintenance, especially since multiple cameras are needed per intersection. In addition, cameras do not work well in adverse weather, at night or in poor lighting, when most traffic crashes occur, and there are many privacy concerns with the data cameras collect.
What about radar?
Traffic data collection is an important tool for cities and towns when decisions need to be made about road systems and many options for collecting traffic data exist. Radar is a popular choice for traffic operations departments that plan and control the movement of vehicles over streets and highways and whose mandate it is to make sure this is done efficiently and safely. Radar can detect the presence of vehicles, allowing traffic operations departments to communicate and make changes to the timing of traffic light signals.
While radar has been used reliably to collect traffic information for many years, there are still drawbacks with its use, including:
- Inability to distinguish between types of road users
- Can only be used to detect and count vehicles
- High cost of hardware, as more than one radar per intersection is required
- Can be expensive to install

As the presence of other types of road users such as cyclists continues to increase, vehicles must share the road with those road users in a safe and efficient manner. The availability of data regarding vulnerable road users is becoming a priority when choosing a method for traffic data collection. Lidar is a multimodal technology that offers reliable traffic data about all road users, with more information than radar can provide. BlueCity combines lidar with AI to give users more information for traffic management at a lower cost, given that it can cover an entire intersection with one sensor compared to the 6 radar sensors required for similar coverage (see below example).
When to use radar
Radar is an excellent option for 24/7 vehicle detection, as it is able to reliably detect vehicles in poor lighting and bad weather. Radar can be used when detailed information about types of road users or safety metrics are not required.
How does BlueCity stack up to radar?
BlueCity, which combines 3D lidar sensors with AI software, is an ideal, cost-effective solution for many municipal departments, including transport planners, operations and road safety departments, and city engineers. BlueCity is an excellent choice when multimodal traffic data collection in all weather and lighting conditions is required.
Lidar sensors capture data anonymously, effectively eliminating concerns regarding private data being collected and stored. What’s more, BlueCity uses artificial intelligence to power advanced safety analytics and offer better visualization of the data captured as well as automated traffic signal performance measures.
Traffic radar FAQ
Q: Can radar help with traffic planning?
A: No. Radar is a method that is used by traffic operations departments to guide decisions about road systems. It cannot provide the type of information required by traffic planners to define future policies, goals, investments and planning designs for future needs. Radar cannot provide multimodal data or advanced safety metrics.
Q: Can radar detect all kinds of road users?
A: No. Radar can only detect the presence of a vehicle. It is not able to distinguish between types of vehicles, for example buses, trucks or motorcycles, nor can it detect the presence of cyclists and pedestrians.
Q: Is radar an expensive solution for traffic data collection?
A: Yes. The hardware costs of installing radar at intersections can be expensive because more than one sensor is needed. Furthermore, to install radar, the ground must be dug up so wires can be installed. This necessitates the closure of roads, which becomes an inconvenience to road users.
Q: Can radar provide 24/7 data collection?
A: Yes. Like lidar sensors, radar is able to provide reliable traffic data 24/7, regardless of the lighting and weather conditions.
Radar summary
Pros: Radar installed at intersections is a great choice because it detects the presence of vehicles in all types of lighting and weather conditions. When it detects the presence of vehicles at an intersection, traffic light timing can be optimized.
Cons: Radar can be an expensive choice because roads need to be dug up in order to install the required wiring, causing road closures and increasing costs. In addition, more than one sensor is needed for each intersection. Radar is also not able to distinguish between the different types of road users or different types of vehicles. While radar can be used as a tool for road system decisions, it cannot be used for traffic planning.
The best alternative: BlueCity Lidar + AI
Ouster BlueCity is a unique, cost-effective solution that allows planners to capture multimodal traffic data in real-time 24/7. Its lidar sensors are easy to install and maintain and most intersections require only one sensor. Unlike cameras, lidar sensors work in all weather and lighting conditions. And compared to radar, lidar excels at detecting and classifying multiple types of road users, rather than just vehicles. BlueCity leverages artificial intelligence to power advanced safety analytics that help proactively identify dangerous intersections and improve road safety.

To learn more about our BlueCity traffic solution, check out our webinar or reach out to us to set up a call with our ITS experts.